|
Radiation Pneumonitis
- Damage to lungs after radiation therapy
- Usually requires at least 4500 rads
- Especially common if >6000 R given in 5-6 weeks
- Occurs more often if there is concurrent or later
chemotherapy
- Pathologic phases
- Exudative phase = edema fluid + hyaline membranes
- Organizing phase
- Fibrotic phase = interstitial fibrosis
- Time of onset
- Usually at least 6 weeks up to 6 months after
treatment
- Location
- Confined to radiation portal
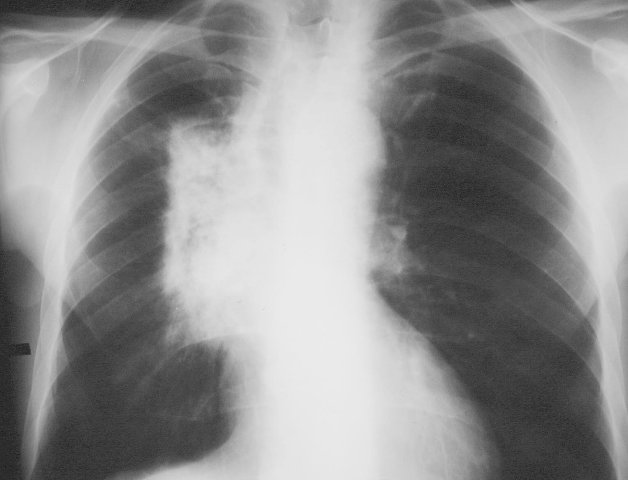 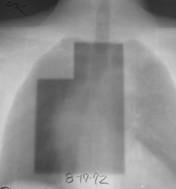
Radiation portal (right) with subsequent radiation pneumonitis (left image).
· Acute Radiation Pneumonitis
o Occurs within 1-8 weeks after radiation therapy
o Pathology
§ Depletion of surfactant (1 week to 1 month later), plasma
exudation, desquamation of alveolar + bronchial cells
o Usually asymptomatic
o When symptomatic
§ Nonproductive cough, shortness of breath, weakness, fever
(insidious onset)
§ Acute respiratory failure (rare)
o Changes usually confined to radiation portal
o Patchy / confluent consolidation, may persist up to 1 month (exudative
reaction)
§ Atelectasis + air bronchogram
§ Spontaneous pneumothorax (rare)
- CT findings of acute radiation pneumonitis
- Homogeneous slight increase in attenuation (2-4
months after therapy)
- Patchy consolidation (1-12 months after therapy)
- Non-uniform discrete consolidation (most common; 3
months to 10 years after therapy)
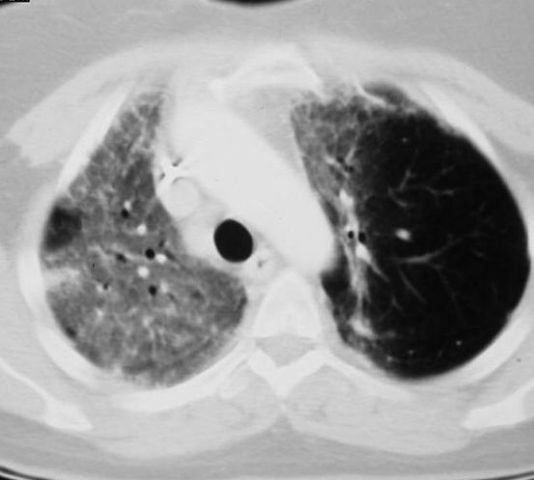 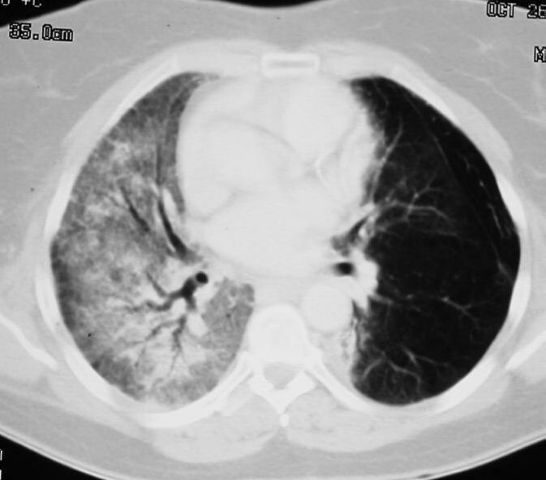 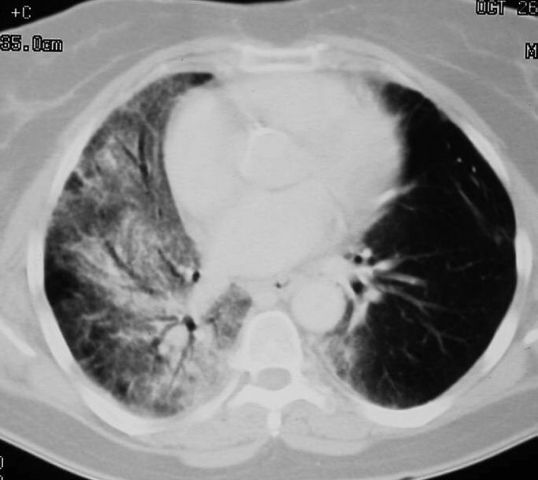
Sequential
transverse images through lung showing radiation pneumonitis in right lung
- Prognosis
- Recovery or progression to death from fibrosis
- Rx
· Chronic Radiation Damage
o 9-12 months after radiation therapy
o Histology
§ Permanent damage of endothelial + type I alveolar cells
o May be associated with:
§ Thymic cyst
§ Calcified lymph nodes (in Hodgkin disease)
§ Pericarditis + effusion (within 3 years)
§ Severe loss of volume
§ Dense fibrous strands from hilum to periphery
§ Thickening of pleura
o CT findings
§ Solid consolidation (radiation fibrosis) + bronchiectasis
(stabilized by 1 year after therapy)
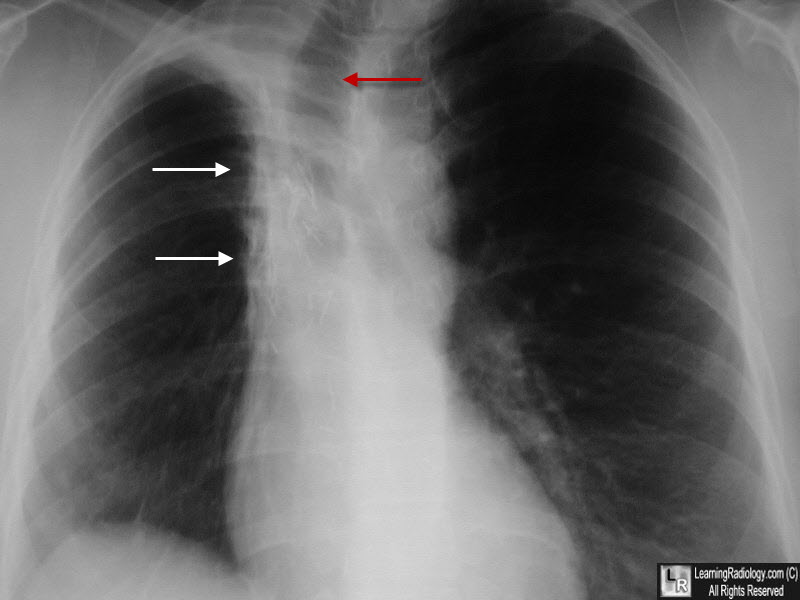
Radiation Fibrosis. There is a zone of increased density in the right paratracheal region with an almost straight edge (white arrows) suggestive of scarring from a radiation portal. The tr4achea is deviated to the right from volume loss (red arrow).
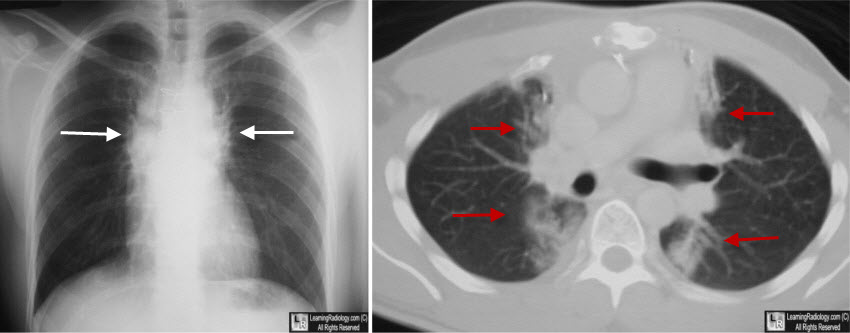
Radiation Fibrosis. The chest radiograph shows bilateral and almost symmetrical densities in a paramediastinal location with unusually well-demarcated edges, suggesting a radiation portal(white arrows). The CT scan demonstrates the same findings with fibrotic stranding seen on both sides of the mediastinum along the path of prior radiation (red arrows).
|